What Does the Florida House of Representatives Do
| Florida Business firm of Representatives | |
|---|---|
| 2020–22 Florida Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Blazon | Lower business firm of the Florida Legislature |
| Term limits | 4 terms (8 years) |
| History | |
| Founded | May 26, 1845 |
| Preceded past | Legislative Council of the Territory of Florida |
| Leadership | |
| Speaker | Chris Sprowls (R) |
| Speaker pro tempore | Bryan Avila (R) |
| Majority Leader | Michael Grant (R) |
| Minority Leader | Evan Jenne (D) |
| Construction | |
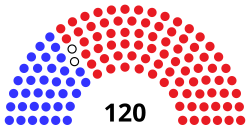
| Seats | 120 |
 | |
| Political groups | Majority
Minority
|
| Length of term | 2 years |
| Say-so | Commodity III, Constitution of Florida |
| Salary | $29,697/year + per diem (Subsistence & Travel)[1] |
| Elections | |
| Final ballot | Nov iii, 2020 (120 seats) |
| Next ballot | Nov 8, 2022 (120 seats) |
| Redistricting | Legislative control |
| Motto | |
| In God Nosotros Trust | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Firm of Representatives Sleeping accommodation Florida Capitol Tallahassee, Florida | |
| Website | |
| Official website | |
The Florida House of Representatives is the lower house of the Florida Legislature, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Florida, the Florida Senate being the upper house. Article 3, Section ane of the Constitution of Florida, adopted in 1968, defines the office of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted.[2] The Business firm is composed of 120 members, each elected from a unmarried-member district with a population of approximately 157,000 residents. Legislative districts are drawn on the basis of population figures, provided by the federal decennial census. Representatives' terms brainstorm immediately upon their election. As of 2022, Republicans hold the majority in the State House with 78 seats; Democrats are in the minority with 40 seats. Two seats are vacant.
Titles [edit]
Members of the Business firm of Representatives are referred to as representatives. Because this shadows the terminology used to describe members of U.S. Business firm of Representatives, constituents and the news media, using The Associated Press Stylebook, often refer to members as land representatives to avert confusion with their federal counterparts.
Terms [edit]
Article III of the Florida Constitution defines the terms for state legislators.
The Constitution requires state representatives to be elected for two-year terms.
Upon election, legislators take office immediately.
Term limits [edit]
On November 3, 1992, almost 77 percent of Florida voters backed Amendment 9, the Florida Term Limits Amendment, which amended the state Constitution, to enact viii-year term limits on federal and state officials. Under the Subpoena, former members can exist elected again after a break.[3] In 1995, the U.South. Supreme Court ruled that states could not enact congressional term limits, but ruled that the country level term limits remain.[iv]
Qualifications [edit]
Florida legislators must be at to the lowest degree twenty-i years old, an elector and resident of their district, and must have resided in Florida for at least 2 years prior to election.[5]
Legislative session [edit]
Each twelvemonth during which the Legislature meets constitutes a new legislative session.
Commission weeks [edit]
Legislators start Commission activity in September of the year prior to the regular legislative session. Because Florida is a role-time legislature, this is necessary to permit legislators fourth dimension to work their bills through the committee process, prior to the regular legislative session.[half dozen]
Regular legislative session [edit]
The Florida Legislature meets in a 60-day regular legislative session each year. Regular legislative sessions in odd-numbered years must begin on the first Tuesday afterwards the first Monday in March. Under the state Constitution, the Legislature tin can begin even-numbered year regular legislative sessions at a time of its choosing.[7]
Prior to 1991, the regular legislative session began in Apr. Senate Articulation Resolution 380 (1989) proposed to the voters a constitutional subpoena (canonical November 1990) that shifted the starting date of regular legislative session from Apr to February. After, Senate Joint Resolution 2606 (1994) proposed to the voters a constitutional amendment (canonical November 1994) shifting the start appointment to March, where it remains. The reason for the "first Tuesday later the first Monday" requirement stems back to the time when regular legislative session began in April. regular legislative session could start whatsoever solar day from April two through Apr 8, just never on April 1 – April Fool'south Day. In contempo years, the Legislature has opted to start in January in social club to allow lawmakers to be home with their families during school spring breaks, and to give more time ahead of the legislative elections in the Fall.[8]
Organizational session [edit]
On the fourteenth solar day post-obit each general election, the Legislature meets for an organizational session to organize and select officers.
Special session [edit]
Special legislative sessions may be called by the governor, past a joint announcement of the Senate president and Business firm speaker, or by a 3-fifths vote of all legislators. During any special session the Legislature may only address legislative concern that is inside the purview of the purpose or purposes stated in the special session declaration.[nine]
Powers and process [edit]
The Florida Firm is authorized past the Florida Constitution to create and improve the laws of the U.S. state of Florida, subject field to the governor's power to veto legislation. To practise so, legislators propose legislation in the forms of bills drafted by a nonpartisan, professional staff. Successful legislation must undergo committee review, iii readings on the floor of each business firm, with appropriate voting majorities, as required, and either be signed into law by the governor or enacted through a veto override canonical by two-thirds of the membership of each legislative business firm.[10]
Its statutes, called "chapter laws" or generically equally "slip laws" when printed separately, are compiled into the Laws of Florida and are called "session laws".[11] The Florida Statutes are the codification statutory laws of the state.[11]
In 2009, legislators filed 2,138 bills for consideration. On boilerplate, the Legislature has passed nearly 300 bills into law annually.[12]
In 2013, the Legislature filed virtually 2000 bills. Nigh 1000 of these are "fellow member bills." The remainder are bills by committees responsible for certain functions, such equally budget. In 2016, about fifteen% of the bills were passed.[13] In 2017, 1,885 lobbyists registered to represent iii,724 entities.[13]
The House besides has the power to advise amendments to the Florida Constitution. Additionally, the House has the exclusive power to impeach officials, who are and then tried by the Senate.
Leadership [edit]
The House is headed by a speaker, elected by the members of the House to a 2-year term. The speaker presides over the House, appoints committee members and commission chairs, influences the placement of bills on the calendar, and rules on procedural motions. The speaker pro tempore presides if the speaker leaves the chair or if there is a vacancy. The speaker, forth with the Senate president and governor of Florida, command most of the agenda of land business organisation in Florida.
The majority and minority caucus each elect a leader.
| Position | Name | Political party | District |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speaker of the Business firm | Chris Sprowls | Republican | 65 |
| Speaker pro tempore | Bryan Avila | Republican | 111 |
| Majority leader | Michael J. Grant | Republican | 75 |
| Minority leader | Evan Jenne | Autonomous | 99 |
Limerick [edit]
| Affiliation | Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) | Full | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Democratic | Vacant | ||||
| End of 2016–18 legislature | 75 | 41 | 116 | 4 | ||
| Commencement of previous (2018–20) legislature | 73 | 47 | 120 | 0 | ||
| Stop of previous legislature | 71 | 45 | 116 | iv | ||
| Start of current (2020–22) legislature | 78 | 42 | 120 | 0 | ||
| January 10, 2022[14] | 41 | 119 | 1 | |||
| Jan eleven, 2022[fifteen] | 40 | 118 | two | |||
| Latest voting share | 66.1% | 33.9% | ||||
Members, 2020–2022 [edit]
| District | Name | Party | Residence | Counties represented | Kickoff Elected[16] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ane | Michelle Salzman | Rep | Pensacola | Part of Escambia | 2020 |
| two | Alex Andrade | Rep | Pensacola | Parts of Escambia and Santa Rosa | 2018 |
| 3 | Jayer Williamson | Rep | Stride | Parts of Okaloosa and Santa Rosa | 2016 |
| 4 | Patt Maney | Rep | Destin | Function of Okaloosa | 2020 |
| five | Brad Drake | Rep | DeFuniak Springs | Holmes, Jackson, Walton, Washington, part of Bay | 2014, 2008–12 |
| half-dozen | Jay Trumbull | Rep | Panama City | Office of Bay | 2014 |
| seven | Jason Shoaf | Rep | Port St. Joe | Calhoun, Franklin, Gulf, Jefferson, Lafayette, Liberty, Madison, Taylor, Wakulla, part of Leon | 2019* |
| 8 | Ramon Alexander | Dem | Tallahassee | Gadsden, part of Leon | 2016 |
| 9 | Allison Tant | Dem | Tallahassee | Role of Leon | 2020 |
| 10 | Chuck Brannan | Rep | Macclenny | Baker, Columbia, Hamilton, Suwannee, role of Alachua | 2018 |
| 11 | String Byrd | Rep | Neptune Beach | Nassau, part of Duval | 2016 |
| 12 | Clay Yarborough | Rep | Jacksonville | Part of Duval | 2016 |
| xiii | Tracie Davis | Dem | Jacksonville | Part of Duval | 2016 |
| 14 | Angie Nixon | Dem | Jacksonville | Part of Duval | 2020 |
| 15 | Wyman Duggan | Rep | Jacksonville | Role of Duval | 2018 |
| xvi | Jason Fischer | Rep | Jacksonville | Part of Duval | 2016 |
| 17 | Cyndi Stevenson | Rep | St. Augustine | Part of St. Johns | 2015* |
| 18 | Sam Garrison | Rep | Orange Park | Role of Clay | 2020 |
| 19 | Bobby Payne | Rep | Palatka | Bradford, Putnam, Union, part of Clay | 2016 |
| 20 | Yvonne Hayes Hinson | Dem | Gainesville | Parts of Alachua and Marion | 2020 |
| 21 | Chuck Clemons | Rep | Newberry | Dixie, Gilchrist, part of Alachua | 2016 |
| 22 | Joe Harding | Rep | Williston | Levy, office of Marion | 2020 |
| 23 | Stan McClain | Rep | Belleview | Part of Marion | 2016 |
| 24 | Paul Renner | Rep | Palm Coast | Flagler, parts of St. Johns and Volusia | 2015* |
| 25 | Tom Leek | Rep | Ormond Beach | Role of Volusia | 2016 |
| 26 | Elizabeth Fetterhoff | Rep | DeLand | Role of Volusia | 2018 |
| 27 | Webster Barnaby | Rep | Deltona | Role of Volusia | 2020 |
| 28 | David Smith | Rep | Winter Springs | Part of Seminole | 2018 |
| 29 | Scott Plakon | Rep | Longwood | Part of Seminole | 2014, 2008–12 |
| 30 | Joy Goff-Marcil | Dem | Maitland | Parts of Orange and Seminole | 2018 |
| 31 | Keith Truenow | Rep | Tavares | Parts of Lake and Orange | 2020 |
| 32 | Anthony Sabatini | Rep | Howey-in-the-Hills | Function of Lake | 2018 |
| 33 | Brett Hage | Rep | Oxford | Sumter, parts of Lake and Marion | 2018 |
| 34 | Ralph Massullo | Rep | Lecanto | Citrus, part of Hernando | 2016 |
| 35 | Blaise Ingoglia | Rep | Spring Loma | Office of Hernando | 2014 |
| 36 | Amber Mariano | Rep | Hudson | Part of Pasco | 2016 |
| 37 | Ardian Zika | Rep | Country o' Lakes | Part of Pasco | 2018 |
| 38 | Randy Maggard | Rep | Zephyrhills | Part of Pasco | 2019* |
| 39 | Josie Tomkow | Rep | Polk City | Parts of Osceola and Polk | 2018* |
| forty | Colleen Burton | Rep | Lakeland | Part of Polk | 2014 |
| 41 | Sam Killebrew | Rep | Wintertime Haven | Part of Polk | 2016 |
| 42 | Fred Hawkins | Rep | St. Cloud | Parts of Osceola and Polk | 2020 |
| 43 | Kristen Arrington | Dem | Kissimmee | Part of Osceola | 2020 |
| 44 | Geraldine Thompson | Dem | Orlando | Part of Orange | 2018 |
| 45 | Kamia Brown | Dem | Orlando | Function of Orangish | 2016 |
| 46 | Travaris McCurdy | Dem | Orlando | Part of Orange | 2020 |
| 47 | Anna Eskamani | Dem | Orlando | Part of Orange | 2018 |
| 48 | Daisy Morales | Dem | Orlando | Role of Orangish | 2020 |
| 49 | Carlos Guillermo Smith | Dem | Orlando | Part of Orange | 2016 |
| 50 | Rene Plasencia | Rep | Orlando | Parts of Brevard and Orange | 2014 |
| 51 | Tyler Sirois | Rep | Cocoa | Function of Brevard | 2018 |
| 52 | Thad Altman | Rep | Rockledge | Part of Brevard | 2016, 2003–08 |
| 53 | Randy Fine | Rep | Melbourne Beach | Function of Brevard | 2016 |
| 54 | Erin Grall | Rep | Vero Embankment | Indian River, part of St. Lucie | 2016 |
| 55 | Kaylee Tuck | Rep | Sebring | Glades, Highlands, Okeechobee, part of St. Lucie | 2020 |
| 56 | Melony Bong | Rep | Fort Meade | DeSoto, Hardee, part of Polk | 2018 |
| 57 | Mike Beltran | Rep | Lithia | Part of Hillsborough | 2018 |
| 58 | Lawrence McClure | Rep | Dover | Role of Hillsborough | 2017* |
| 59 | Andrew Learned | Dem | Brandon | Function of Hillsborough | 2020 |
| threescore | Jackie Toledo | Rep | Tampa | Office of Hillsborough | 2016 |
| 61 | Dianne Hart | Dem | Tampa | Role of Hillsborough | 2018 |
| 62 | Susan Valdes | Dem | Tampa | Role of Hillsborough | 2018 |
| 63 | Fentrice Driskell | Dem | Tampa | Part of Hillsborough | 2018 |
| 64 | Traci Koster | Rep | Tampa | Parts of Hillsborough and Pinellas | 2020 |
| 65 | Chris Sprowls | Rep | Palm Harbor | Part of Pinellas | 2014 |
| 66 | Nick DiCeglie | Rep | Indian Rocks Beach | Part of Pinellas | 2018 |
| 67 | Chris Latvala | Rep | Clearwater | Part of Pinellas | 2014 |
| 68 | Ben Diamond | Dem | St. Petersburg | Part of Pinellas | 2016 |
| 69 | Linda Chaney | Rep | St. Pete Embankment | Part of Pinellas | 2020 |
| 70 | Michele Rayner | Dem | St. Petersburg | Parts of Hillsborough, Manatee, Pinellas, Sarasota | 2020 |
| 71 | Volition Robinson | Rep | Bradenton | Parts of Manatee and Sarasota | 2018 |
| 72 | Fiona McFarland | Rep | Sarasota | Parts of Sarasota | 2020 |
| 73 | Tommy Gregory | Rep | Sarasota | Parts of Manatee and Sarasota | 2018 |
| 74 | James Buchanan | Rep | Osprey | Part of Sarasota | 2018 |
| 75 | Michael J. Grant | Rep | Port Charlotte | Charlotte | 2016, 2004–08 |
| 76 | Adam Botana | Rep | Bonita Springs | Function of Lee | 2020 |
| 77 | Mike Giallombardo | Rep | Greatcoat Coral | Part of Lee | 2020 |
| 78 | Jenna Persons | Rep | Fort Myers | Function of Lee | 2020 |
| 79 | Spencer Roach | Rep | North Fort Myers | Part of Lee | 2018 |
| 80 | Lauren Melo | Rep | Naples | Hendry, part of Collier | 2020 |
| 81 | Kelly Skidmore | Dem | Boca Raton | Part of Palm Embankment | 2006–ten, 2020 |
| 82 | John Snyder | Rep | Palm Metropolis | Parts of Martin and Palm Beach | 2020 |
| 83 | Toby Overdorf | Rep | Palm City | Parts of Martin and St. Lucie | 2018 |
| 84 | Dana Trabulsy | Rep | Fort Pierce | Office of St. Lucie | 2020 |
| 85 | Rick Roth | Rep | Loxahatchee | Part of Palm Beach | 2016 |
| 86 | Matt Willhite | Dem | Wellington | Role of Palm Beach | 2016 |
| 87 | David Silvers | Dem | West Palm Beach | Part of Palm Beach | 2016 |
| 88 | Vacant [fourteen] | Part of Palm Beach | |||
| 89 | Mike Caruso | Rep | Delray Beach | Role of Palm Beach | 2018 |
| xc | Joseph Casello | Dem | Boynton Beach | Role of Palm Beach | 2018 |
| 91 | Emily Slosberg | Dem | Boca Raton | Part of Palm Beach | 2016 |
| 92 | Patricia Hawkins-Williams | Dem | Lauderdale Lakes | Function of Broward | 2016 |
| 93 | Chip LaMarca | Rep | Lighthouse Point | Function of Broward | 2018 |
| 94 | Vacant [15] | Role of Broward | |||
| 95 | Anika Omphroy | Dem | Lauderdale Lakes | Role of Broward | 2018 |
| 96 | Christine Hunschofsky | Dem | Parkland | Part of Broward | 2020 |
| 97 | Dan Daley | Dem | Coral Springs | Role of Broward | 2019* |
| 98 | Michael Gottlieb | Dem | Davie | Office of Broward | 2018 |
| 99 | Evan Jenne | Dem | Hollywood | Function of Broward | 2014 |
| 100 | Joe Geller | Dem | Aventura | Parts of Broward and Miami-Dade | 2014 |
| 101 | Marie Woodson | Dem | Hollywood | Part of Broward | 2020 |
| 102 | Felicia Robinson | Dem | Miami Gardens | Parts of Broward and Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 103 | Tom Fabricio | Rep | Miramar | Parts of Broward and Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 104 | Robin Bartleman | Dem | Weston | Office of Broward | 2020 |
| 105 | David Borrero | Rep | Sweetwater | Parts of Broward, Collier, and Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 106 | Bob Rommel | Rep | Naples | Part of Collier | 2016 |
| 107 | Christopher Benjamin | Dem | Miami Gardens | Part of Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 108 | Dotie Joseph | Dem | North Miami | Part of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 109 | James Bush-league | Dem | Miami | Part of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 110 | Alex Rizo | Rep | Hialeah | Function of Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 111 | Bryan Avila | Rep | Hialeah | Part of Miami-Dade | 2014 |
| 112 | Nicholas Duran | Dem | Miami | Part of Miami-Dade | 2016 |
| 113 | Mike Grieco | Dem | Miami Beach | Part of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 114 | Demi Busatta Cabrera | Rep | Coral Gables | Role of Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 115 | Vance Aloupis | Rep | Miami | Role of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 116 | Daniel Perez | Rep | Miami | Part of Miami-Dade | 2017* |
| 117 | Kevin Chambliss | Dem | Florida City | Part of Miami-Dade | 2020 |
| 118 | Anthony Rodriguez | Rep | Miami | Part of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 119 | Juan Fernandez-Barquin | Rep | Kendale Lakes | Part of Miami-Dade | 2018 |
| 120 | Jim Mooney | Rep | Islamorada | Monroe and part of Miami-Dade | 2020 |
*Elected in a special ballot.
District map [edit]

Districts and political party composition of the Florida Business firm of Representatives after the 2022 elections
Democratic Political party
Republican Party
By composition of the House of Representatives [edit]
From 1874 to 1996, the Autonomous Party held majorities in the Florida Business firm of Representatives. Post-obit sizable GOP gains in the 1994 election, which significantly reduced the Autonomous Political party majority in the Florida Firm, Republicans captured a majority in the 1996 ballot. The Republican Party has been the majority party since that fourth dimension in the Business firm.
Additional data on the past composition of the Florida House of Representatives tin be found in Allen Morris's The Florida Handbook (various years, published every two years for many years).
See also [edit]
- Florida Autonomous Party
- Elections in Florida
- Florida Land Capitol
- Regime of Florida
- List of speakers of the Florida House of Representatives
- Republican Party of Florida
- The Florida Channel
References [edit]
- ^ "The 2022 Florida Statutes F.S. 11.13 Compensation of members". Florida Legislature.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION OF THE Country OF FLORIDA". Florida Legislature. Archived from the original on December eight, 2008. Retrieved December 7, 2017.
- ^ "Vote Yes On Amendment No. 9 To Begin Limiting Political Terms". Sun-Sentinel.
- ^ "Florida Backs Article 5 Convention for Constitutional Amendment on Congressional Term Limits". Sunshine State News.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION OF THE Land OF FLORIDA". Florida Legislature.
- ^ "Editorial:Advice to Legislature:Pursue express calendar". Florida Today.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION OF THE STATE OF FLORIDA". Florida Legislature.
- ^ Buzzacco-Foerster, Jenna (February eighteen, 2016). "Proposal to move 2022 session to January heads Business firm floor". Florida Politics . Retrieved February xviii, 2016.
- ^ "The Florida Constitution". Florida Legislature.
- ^ "The Florida Senate Handbook" (PDF). Florida Senate.
- ^ a b "Statutes & Constitution: Online Sunshine". Florida Legislature. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ^ Flemming, Paul (March 8, 2009). Capital Ideas: Lawmakers confront 2,138 proposals. Florida Today.
- ^ a b Cotterell, Bill (March 7, 2017). "Legislative session by the numbers". Florida Today. Melbourne,Florida. pp. 5A.
- ^ a b Democrat Omari Hardy (District 88) resigned effective this date to run for a special election in the 20th congressional commune. Man, Anthony (July 28, 2021). "Five elected officials have resigned so they tin can run for Congress in South Florida special election". South Florida Sun Sentinel . Retrieved January 11, 2022.
- ^ a b Democrat Bobby DuBose (District 94) resigned effective this appointment to run for a special election in the 20th congressional commune. Human being, Anthony (July 28, 2021). "Five elected officials take resigned and then they tin run for Congress in South Florida special election". Due south Florida Sun Sentinel . Retrieved January 11, 2022.
- ^ And previous terms of service, if any.
External links [edit]
- Official Site Florida House
- Official Site Florida Elections Division
- The Firm Journal, the official record of deportment taken by the House and its committees, total text online in the University of Florida's Digital Collections
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Florida_House_of_Representatives
0 Response to "What Does the Florida House of Representatives Do"
Post a Comment